2025年5月,浙江财经大学管理学院“数智决策研究中心”的孙琪老师完成的论文“A self-esteem driven feedback mechanism with diverse power structures to prevent strategic manipulation in social network group decision making”在国际期刊Information Sciences发表。Information Sciences是一本专注于信息科学与技术领域的国际学术期刊,2025年影响因子为6.8,属于JCR一区期刊,也是CCF-B类期刊。论文的工作受到了国家自然科学基金、浙江省自然科学基金等项目的支持。

论文针对社交网络群体决策中权力结构的分布和策略性操纵行为对决策公平性和效率带来的挑战,提出了一个新的共识理论框架,专门设计用于分析权力结构并防止社交网络群体决策中的策略性操纵行为。该框架提出了基于中心性度量的影响力的指数和基于结构洞与图密度的权力指数,分别用于识别社交信任网络中的意见领袖和子群的权力动态。接着,论文提出了一个基于最大熵模型来探索社交网络群体决策中的权力动态偏好聚合。此外,论文还引入了一个基于边界最大共识度的反馈模型,解决了现有共识方法往往忽视的问题,包括决策者的自尊和操纵行为的风险。该模型在调整偏好时考虑了子群的自尊,旨在防止潜在的策略性操纵,增强决策的公平性和效率。最后,通过彻底的数值评估和比较评估来证实所提出方法的有效性。实验结果表明,集中的权力可以加快共识形成,但可能损害公平性,而分散的权力虽然减慢共识,却增加了参与度和多样性,降低了权力滥用的风险。
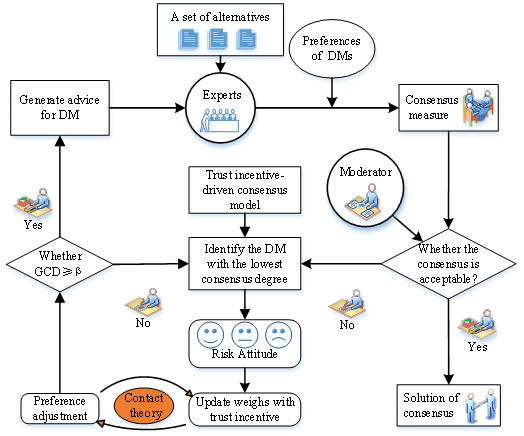
图1:论文所提方法的主要框架
全文链接:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020025524017377?via%3Dihub
论文摘要:
In social network group decision-making (SNGDM), the distribution of power structures and strategic manipulation behaviors pose challenges to the fairness and efficiency of thedecision makingprocess. This paper introduces a novel consensus theoretical framework, specifically designed for analyzing power structures and preventing strategic manipulation behavior in SNGDM. It proposes a centrality measures-based influence index and a structural holes and graph density-based power index, respectively, to identify opinion leaders and power dynamics of subgroups in social trust networks. Then, a maximum entropy-based model is presented to explore power dynamics for preference aggregation in SNGDM. Furthermore, this paper introduces a feedback model based on the boundary maximum consensus degree, addressing issues that existing consensus methods tend to overlook, including the self-esteem of decision-makers and the risks of manipulation behavior. The model considers the self-esteem of subgroups when adjusting preferences, aiming to prevent potential strategic manipulation and enhance the fairness and efficiency of decision-making. Finally, thorough numerical evaluations and comparative assessments have been conducted to substantiate the effectiveness of the proposed methodology. Experiment results show that concentrated power can speed up consensus formation but may harm fairness, while dispersed power, although it slows consensus, increases participation and diversity, reducing the risk of power abuse.
作者简介:
孙琪,浙江财经大学管理学院讲师,主要研究方向为群智决策、群体共识及社会网络分析等。主持浙江省自然科学基金青年项目1项,在IEEE Transactions onFuzzySystems、Knowledge-Based Systems、InformationScience、Expert Systems with Applications、Artificial Intelligence Review等国内外重要学术期刊和国际会议上发表学术论文10余篇。
引用信息:
Q. Sun X. Zhang, F. Chiclana, F. X. Ji, Q. Q. Long, J. Wu. A self-esteem driven feedback mechanism with diverse power structures to prevent strategic manipulation in social network group decision making, 2025, 700: 121823.

